
It seems that Ford are having a lot of early 1.6L Duratorq-TDCI diesel (both 90 PS/110 PS) turbocharger failure problems. Fiesta, Focus and C-Max are affected. Originally turbo’s would be replaced only to fail again in quick succession. After investigation it appears that the turbo oil feed pipe, over time, sludge’s up and restricts the oil supply.
Now you would think that having identified a potential cause of catastrophic failure of the turbo, which can then trash the rest of the engine, Ford would be breaking every bone in their body to inform owners. No such thing. Apparently they wait until your turbo actually blows then spend 5 hours cleaning affected parts before replacing the oil feed pipe and turbo. What this costs is not worth thinking about.
Now it may be that people have not been using the correct oil, or oil/filters have not been changed as required, I don’t know. But it seems to me that for the cost of fitting a new oil feed pipe the potential threat of impending bankruptcy could be eliminated. I will, when the weather improves, be considering replacing the pipe.
Citroën wrote:
It is necessary to follow a specific oil change procedure on all DV6 and DV6U engines so as to ensure that no used oil remains to mix with the new oil.
The following method must be used:
• The engine oil temperature must be at least 50°C :
• the engine oil temperature is considered to be at 50°C when the water temperature indicator is between 80°C and 90°C or the cooling fan has cut in
• ensure that the vehicle is level (side to side and fore and aft)
• remove the oil filter to allow the circuit to drain completely
• remove the oil filler cap and the dipstick
• remove the drain plug
• allow the oil to drain by gravity for at least 10 minutes (DO NOT USE SUCTION METHODS)
• fit a new oil filter
• refit the drain plug with a new sealing washer
• fill the engine with quantity of oil recommended for the engine
• refit the oil filler cap and the dipstick
• run the engine at idle until the oil pressure warning lamp goes out (about 1 minute)
• wait 5 minutes
• check the oil level using the dipstick: the level should be as close as possible to, but not exceeding the maximum mark (1) so as to be between (1) and (3)
For information, the lower mark (2) = Min (0%) the upper mark (1) = Max (100%) the intermediate mark (3) = 3
4 of 4
CONSEQUENCES OF NOT KEEPING TO THE OIL CHANGE INTERVALS
If the customer does not have the oil changed at the recommended intervals, the oil will become excessively polluted and will no longer ensure the correct lubrication of the engine. One of the first consequences is inadequate lubrication of the turbocharger bearings causing a failure which is repeated after the turbocharger is replaced. Subsequent symptoms resulting from the reduced level of lubrication will be a noisy engine and then destruction of the engine.
We remind you that if the customer does not keep to the servicing intervals recommended in the Maintenance and Guarantee Guide, the customer will be responsible for the durability of the mechanical parts of the engine.
In this case, the any related repairs needed are not covered by the new vehicle warranty.
More:
CONSEQUENCES OF NOT FOLLOWING THE OIL CHANGE PROCEDURE
If the oil changes are not done as described above, all deposits of old oil will not be removed and will very quickly pollute the new oil, accelerating the ageing of the oil in the engine lubrication circuit (even causing the oil to congeal).
The consequences for the engine are the same as if the oil change intervals are not observed. As a result, any related repairs needed are not covered under the new vehicle warranty.
Jak często wymieniać olej, jakiej marki olej jest najlepszy?
Turbosprężarka wymaga oleju dobrej jakości. Zalecamy półsyntetyczny lub syntetyczny olej znanych, dobrych marek. Wymiany oleju dokonujemy w odstępach zalecanych przez producenta pojazdu.
Na jak długo wystarcza turbo?
Na około 200 tys. kilometrów przy dobrej eksploatacji reszty podzespołów.
Czy mogę dopasować turbo z innego samochodu?
Nie - prawie wszystkie turbosprężarki różnią się w środku, nawet jeśli wydają się podobne na zewnątrz. Np. Garrett GT 17 to nazwa grupy turbosprężarek a nie pełna specyfikacja.
Czy mogę dopasować zawór upustowy?
Zawór upustowy powoduje zmniejszenie presji sygnału do siłownika akulatora. To powoduje zwiększenie ciśnienia doładowania, również zawór typu actuator lub westgate powinien być skalibrowany.
Czy można samemu zreperować turbinę?
Nigdy nie próbuj! Układ wirujący musi być wyważony i doważony dynamicznie!!!
Czym spowodowane jest nagromadzenie węgla (wypalony olej) na pierścieniu, rowkach wałka turbiny i łożyska?
Za ten stan rzeczy odpowiada zbyt wysoka temperatura spalin lub zbyt szybkim wyłączaniem silnika po pracy, może to być np. zablokowany system odprowadzania oleju, niesprawne wtryskiwacze, zablokowany lub zużyty filtr powietrza.
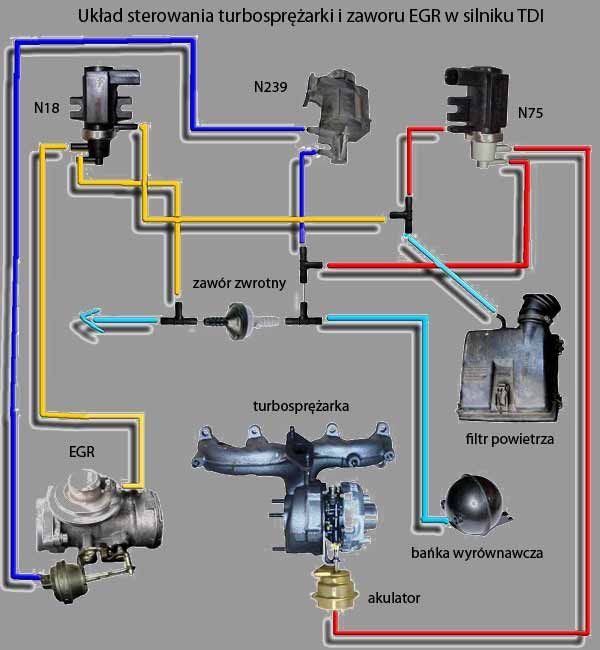
Który z podzespołów jest najczęstszą przyczyną uszkodzenia turbosprężarki?
- pompa oleju,
- vac pompa
- nieszczelny układ dolotowy
- intercooler
- układ podciśnień NP: N18, N239, N75
- EGR
- mapsensor
- przepływomierz
- mechanik - ciała obce wpadające przy wymianie filtra powietrza
- świece
- chłodniczka EGR
- zawór zwrotny podciśnienia
- zapchany kolektor dolotowy
- chip tuning
One turbo application which is hot in the aftermarket is the 763420-0002/3/5 and 40173.07506 fitted to the Peugeot / Citroen and Ford 1,6L DV6TED4 engine.
Customers are experiencing a very high return of original now or teconditioned turbochargers which are creating a high level of warranty. The problems are being created by a high carbon build up In the engine whore the oil level is allowed to run low, this leads to poor oil quality and low outlow which in turn loads to turbo failure.
The carbon build up is very difficult to remove from the engine and involves a complete clean up of the oil pump, oil sump and a change of turbo oil feed pipe. Many vehicle owners are reluctant to pay for this extra work on top of the cost of a new turbo and the result is a second failed turbo, It is extremely important to make your customer aware of this prior to selling or repairing the turbo to avoid warranty claims, Many customers are supplying an oil feed pipe and information leaflet with each turbo to try and tackle the problem.

For the 763420 turbo, to help make the turbo more robust, It Is possible to change the shaft and wheel and thrust iconfiguration from small ID journal bowing (1102-015-103) and small pad thrust bearing (1102-015-770) to standard ID Journal bearing (1102-015-101) and large pad thrust bearing (1102-015-780) by using 1102-015-441. This shaft is actually from the 740661-2/3 Hyundai application. The wheel head and profile are Identical to the 783420 wheel but it is fitted with a standard 0115 straight shaft allowing standard 0115 repair parts to be used. All piece parts parts are now available in ScrollProducts.
Service Update:
Turbocharger failure on the VAG 2.0L TDI with engine code BKD or BKP is a common problem. Clients who experience turbocharger failure should isolate the problem before installing a second replacement turbocharger.
Suspect Problem:
Cylinder Head Crack
Oil Pump/Mechanism
Both of these problems can cause serious damage to the turbocharger internal components. Many clients experience problems with the VW 2.0L TDI "BKD" engine which has known issues with the cylinder head cracking. The crack leaks coolant into the turbocharger causing what is referred to as "hydro-lock" causing the turbine to expand making contact with the housing.
In-proper service & inspection of any turbocharged auto is the key root to secondary replacement failure.
If you have questions regarding a similiar situation feel free to contact
This email address is being protected from spambots. You need JavaScript enabled to view it.
SP Staff
Swirl flaps and the problems they may cause first began to be raised as a possible problem to BMW car owners on 14th June 2007 by members of BMWLand, so members wanted to prevent costly repair bills.
 The BMW inlet manifold have swirl flaps which are designed to create a swirl of air to improve combustion under light load and to reduce a slight increase in emissions from soot due to a lack of air. The flap is closed by an actuator during light load, idling and fully open during engine load to maximise air intake and increase engine output.
The BMW inlet manifold have swirl flaps which are designed to create a swirl of air to improve combustion under light load and to reduce a slight increase in emissions from soot due to a lack of air. The flap is closed by an actuator during light load, idling and fully open during engine load to maximise air intake and increase engine output.
The problem with swirl flaps is that when they fail, the rivets/screws can get sucked into the engine causing damage to pistons, valves, cylinder heads and damage to the turbo which results in several thousand pounds worth of repairs.
BMW introduced an improved and stronger swirl flaps to address the issue in 2004, however there have been reports of the newer design failing and this obviously becomes more of a risk as cars start to come to the end of their warranty.
BMW swirl flap failure can result in a repair bill of several thousand pounds and there are many reported incidents of BMW swirl flap failure on the internet. There are three options for BMW swirl flaps if BMW car is out of warranty:
1) Leave the swirl flaps as they are and hope they don't fail
2) Every two years buy a new manifold to keep it within BMW warranty
3) Buy swirl flap blanking plates and have peace of mind that nothing can fall off & get sucked in to your engine
source: http://www.bmwswirlflaps.co.uk/

There is an obvious problem related to turbo failure on the Renault 1.9dci engines. The root of this problem is related to an EGR design flaw where the valve becomes intermittent. The system itself works fine if the engine is serviced using the recommended Renault schedule and correct engine oil. Unfortunately to many owners fall victim to this problem from ill advise or improperly trained mechanics.
The EGR valve returns unburned fuel back into the cylinder to reduce carbon emissions. The 1.9dci engine is susceptible to a "sticky" EGR, this EGR works using an electric motor as the actuator and becomes unstable. In combination with a secondary fault such as an control valve fault possibly an intercooler leak will overspeed the turbine shaft under heavy load conditions.
When the EGR valve fails, its possible for the turbo cartridge to overheat causing a failure of its seals. When the journal bearings fail the shaft become unstable and the turbine shaft no longer functions. The center catridge has 2-3bar of oil from the oil pump, as the turbo fails the engine wants air but the turbo is now a restriction the pressurized oil pumps into the intake manifold and the engine begins to "RUN AWAY" This is a serious problem for all 1.9dci and 2.2dci engines. A full inspection of the engine must be initiated to locate possible damage.
Renault addressed this issue 2003+ dCi engines and it's common knowledge at this point that this engine needs close service intervals to reduce future failure. Searching the internet will only offer suggestions, bring your car to a professional get the job done properly.
Honeywell’s introduced the VNT in early the 1990s. The system use a turbine housing that can change its internal configuration to adapt to variations in the engine’s air boost requirements. This enables the turbocharger to supply greater engine boost at lower speeds than a smaller unit and behave like a larger turbo at higher speeds. VNT turbo also help to control the emission of NO from diesel vehicles by the use of EGR - Exhaust Gas Recirculation in the engine.
This new platform had several high performance innovations – a new vane shape, a new generation turbine wheel and better controllability delivering 130% of second generation VNT™ boos levels at just 90% of back pressure.
To meet the customer’s needs for smaller, cleaner and better performing engines new type of cartridge was developed which doesn’t not use the turbine housing as a mechanism holder, this housing can be more readily made out of sheet metal material.
Dual Stage systems are being applied to passenger cars in serial-sequential or parallel-sequential configurations. In a serial sequential system, a smaller turbo works in high pressure in advance of a much larger turbo. In a parallel sequential system, two small turbos work side by side.
In a typical application of 4 cylinders, a parallel-sequential system creates up to 30 % more torque compared to its 2.2 liter baseline diesel counterpart. The fuel consumption improvement ranges about 5 percent.
Turbosprężarka jest zaprojektowana z myślą o wysokiej trwałości i niezawodności, jest zintegrowana z silnikiem i powinna pracować przez cały okres jego eksploatacji. Większość awarii z nią związanych źródło swoje bierze w nieprawidłowej pracy bądź konserwacji silnika. Stąd też tak ważna jest okresowa wymiana oleju, konserwacja systemu filtracji oleju, ciśnienia, jak również kontrola systemu filtracji powietrza.
Tylko w nielicznych przypadkach przyczyną problemu jest turbosprężarka - dlatego po wymianie turbosprężarki dochodzi często do stwierdzenia, że nie była ona przyczyną usterki, a problem nadal istnieje.
Najczęściej awarie powstają w wyniku zanieczyszczenia oleju, poprzez ograniczone smarowanie oraz zanieczyszczenia w układzie wydechowym i dolotowym. Te ostatnie są efektem niesprawnego funkcjonowania układu dolotowego, powstają także podczas montażu i charakteryzują się zazwyczaj widocznym uszkodzeniem turbiny.
| Objawy | Przyczyny | Sposoby naprawy |
|
Zanieczyszczony wkład filtra powietrza | Wymienić wkład filtra powietrza na zalecany przez producenta |
|
Niedrożny przewód ssący turbosprężarki | Oczyścić lub wymienić przewód |
|
Niedrożny przewód łączący turbosprężarkę z kolektorem ssącym | Oczyścić lub wymienić przewód |
|
Niedrożny kolektor ssący | Oczyścić kolektor |
|
Nieszczelność pomiędzy filtrem powietrza i turbosprężarką | Usunąć nieszczelność |
|
Nieszczelność pomiędzy turbosprężarką a kolektorem ssącym | Usunąć nieszczelność |
|
Nieszczelność pomiędzy kolektorem ssącym a silnikiem | Usunąć nieszczelność |
|
Zanieczyszczenie w kolektorze wydechowym | Oczyścić kolektor |
|
Ograniczenie drożności układu wydechowego | Usunąć ograniczenie lub wymienić uszkodzone części na nowe (sprawdzić poprawność działania hamulca górskiego) |
|
Uszkodzenie kolektora wydechowego, uszkodzenie lub brak uszczelki | Usunąć nieszczelność lub wymienić uszkodzony kolektor |
|
Nieszczelność pomiędzy turbosprężarką a układem a kolektorem wydechowym | Usunąć nieszczelność |
|
Nieszczelność rury wydechowej lub tłumika | Usunąć nieszczelność lub wymienić uszkodzone części |
|
Niedrożny przewód odprowadzający olej z turbosprężarki | Usunąć niedrożność lub wymienić przewód na nowy |
|
Niedrożny układ odpowietrzający skrzynię korbową silnika | Oczyścić lub wymienić zgodnie z instrukcją |
|
Kanały olejowe korpusu środkowego zanieczyszczone spalonym olejem | Wymienić olej, filtr oleju, oddać turbosprężarkę do naprawy |
|
Pompa wtryskowa lub wtryskiwacze nieprawidłowo wyregulowane | Wyregulować i wymienić zużyte części zgodnie z instrukcją |
|
Nieprawidłowa regulacja luzów zaworowych | Wyregulować i wymienić zużyte części zgodnie z instrukcją |
|
Zużyte gładzie cylindrów i pierścienie | Naprawić silnik zgodnie z instrukcją |
|
Zużyte tłoki, zawory | Naprawić silnik zgodnie z instrukcją |
|
Zanieczyszczona obudowa i koło kompresora | Sprawdzić szczelność układu ssącego powietrza, sprawdzić układ odpowietrzający skrzynię korbową, wymienić olej, filtr oleju, oddać turbosprężarkę do przeglądu |
|
Turbosprężarka uszkodzona | Usunąć przyczyny awarii, oddać turbosprężarkę do naprawy lub wymienić na nową |

-